The Other Properties of a Control
The Other properties of a
control are properties that did not fit neatly into any other category.
This does not mean that they are unimportant. In fact, you can find
some of the most important and useful control properties under the
Other properties of a control. To access these properties, select the
control, invoke the Properties window, and then click the Other tab of
the Properties window (see Figure 6). Let’s take a look.
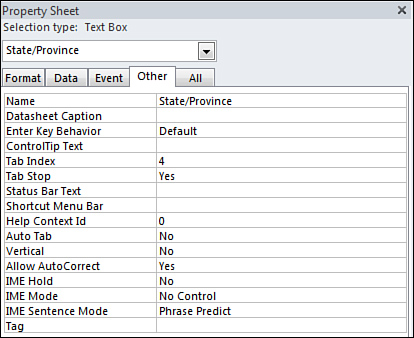
Name— The Name
property allows you to name a control. You use the name that is set in
this property when you refer to the control in code, and this name is
also displayed in various drop-down lists that show all the controls on
a form. It’s important to name controls because named controls improve
the readability of code and make working with Access forms and other
objects easier.
Status Bar Text— The Status Bar Text
property specifies the text that appears in the status bar when a
control gets focus. The setting of this property overrides the Description property that you can set in a table’s design.
Enter Key Behavior— The Enter Key Behavior
property determines whether the Enter key causes the cursor to move to
the next control or to add a new line in the current control. You will
often change the setting of this property for text boxes that you use
to display the contents of memo fields.
Allow AutoCorrect— The Allow AutoCorrect
property specifies whether the AutoCorrect feature is available in a
control. The AutoCorrect feature automatically corrects common spelling
errors and typos.
Vertical— The Vertical
property is used to control whether the text in a control is displayed
horizontally or vertically. The default setting is No, or horizontal.
When you select Yes (vertical display), Access rotates the text in the
control 90 degrees (see Figure 7).

Auto Tab— When the Auto Tab
property is set to Yes, the cursor automatically advances to the next
control when the user enters the last character of an input mask. Some
users like this option, and others find it annoying, especially if they
must tab out of some fields but not others.
Default— The Default
property applies to a command button or to an ActiveX control and
specifies whether the control is the default button on a form.
Cancel— The Cancel
property applies to a command button or to an ActiveX control. It
indicates that you want the control’s code to execute when the user
presses the Esc key while the form is active.
Status Bar Text— The Status Bar Text property specifies the message that appears in the status bar when a control has the focus.
Tab Stop— The Tab Stop
property determines whether the user can use the Tab key to enter a
control. It’s appropriate to set this property to No for controls whose
values rarely get modified. The user can opt to click in the control
when necessary.
Tab Index— The Tab Index property sets the tab order for a control. I generally set the Tab Index
property by using the Tab Order button found in the Tools group on the
Design tab of the Ribbon rather than by setting the value directly in
the control’s Tab Index property. This allows me to set the tab order graphically, which is more intuitive, easier, and saves me a lot of time.
ControlTip Text— The ControlTip Text
property specifies the ToolTip associated with a control. The ToolTip
automatically appears when the user places the mouse pointer over the
control and leaves it there for a moment.
Tag— The Tag property is used to store information about a control. Your imagination determines how you use this property. The Tag property can be read and modified at runtime.